Interval & Sweep Line Related Problems
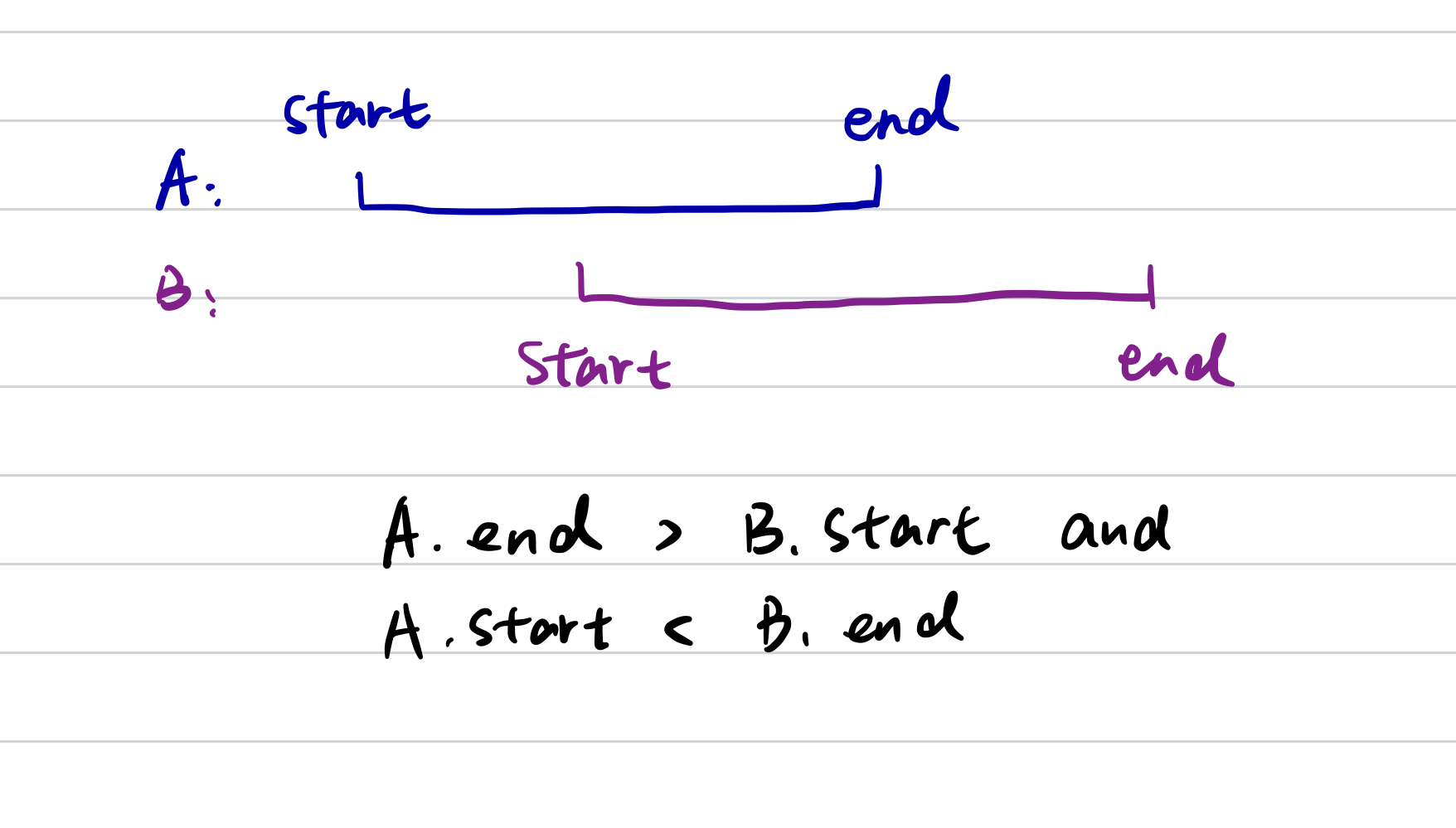
For two intervals, A and B:
- if A.end > B.start and
- A.start < B.end
then they have duplicate intervals.
After sorting by the start time, we are sure that A.start < B.end, which means if A.end > B.start then they have duplicate intervals.
252. Meeting Rooms
Given an array of meeting time intervals consisting of start and end times[s1,e1],[s2,e2],…, determine if a person could attend all meetings.
We can sort the intervals by the starting time. Then go through the meetings one by one and make sure that each meeting ends before the next one starts.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class Solution:
def canAttendMeetings(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
intervals.sort(key = lambda x: x[0])
for i in range(len(intervals) - 1):
if intervals[i][1] > intervals[i+1][0]:
return False
return True
56. Merge Intervals
Given an array of intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], merge all overlapping intervals, and return an array of the non-overlapping intervals that cover all the intervals in the input.
This problem is similar with the Meeting Rooms problem, except for we need to merge when we find the duplicated part.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class Solution:
def merge(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
intervals.sort(key = lambda x: x[0])
res = []
for i in range(len(intervals)):
if not res or res[-1][1] < intervals[i][0]:
res.append(intervals[i])
else:
res[-1][1] = max(res[-1][1], intervals[i][1])
return res
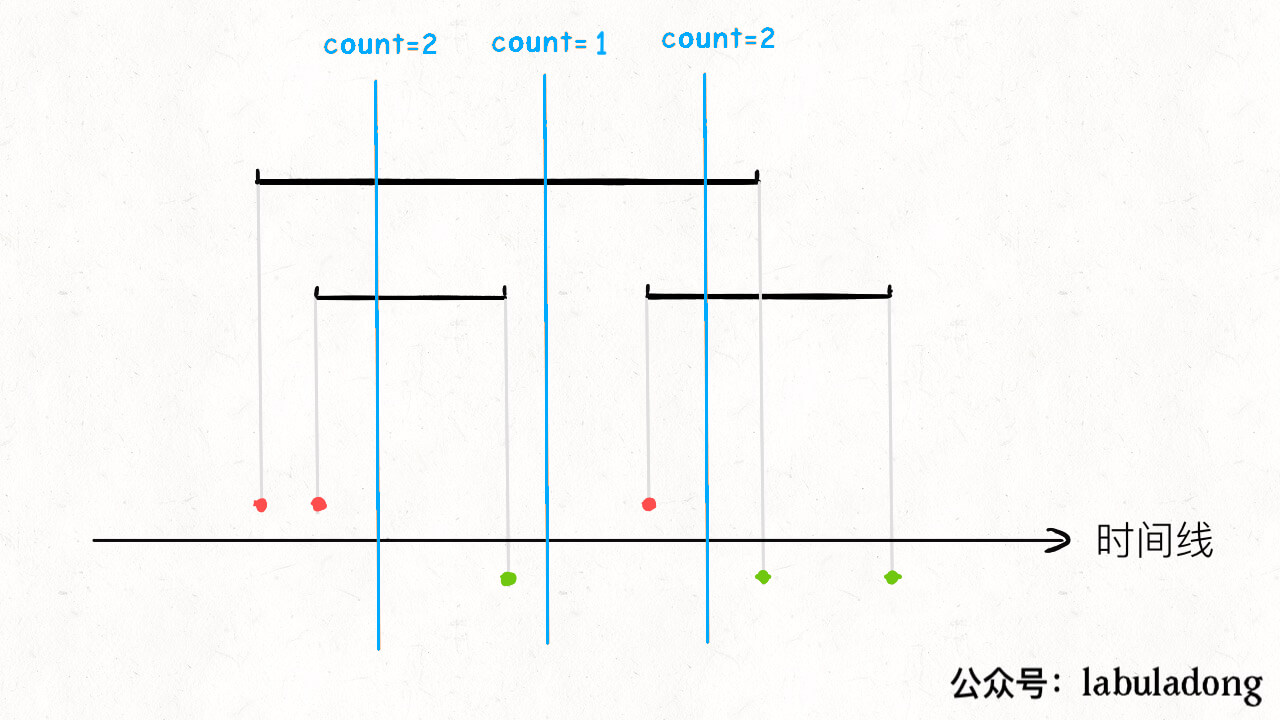
253. Meeting Rooms II
Given an array of meeting time intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], return the minimum number of conference rooms required.
We can use swipe line for this question.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class Solution:
def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not intervals:
return 0
start_timings = sorted(interval[0] for interval in intervals)
end_timings = sorted(interval[1] for interval in intervals)
start = end = 0
count = 0
max_lap = 0
while start < len(intervals) and end < len(intervals):
start_timing, end_timing = start_timings[start], end_timings[end]
if start_timing <= end_timing :
count += 1
start += 1
if end_timing <= start_timing:
count -= 1
end += 1
max_lap = max(max_lap, count)
return max_lap
Follow Up Question
-
Return the interval which is max overlapped. we can store the start time whenever we meet the maximum count, and the end time is the next first end time we meet.
-
Google: Given a list of intervals calendar and a number of available conference rooms. For each query, return true if the meeting can be added to the calendar successfully without causing a conflict, otherwise false. A conference room can only hold one meeting at a time.
Input: calendar = [[1, 2], [4, 5], [8, 10]], rooms = 1, queries = [[2, 3], [3, 4]]
Output: [true, true]
57. Insert Interval
Given an existing non-overlapping interval list sorted by start, insert a new interval into it, merge if needed.
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
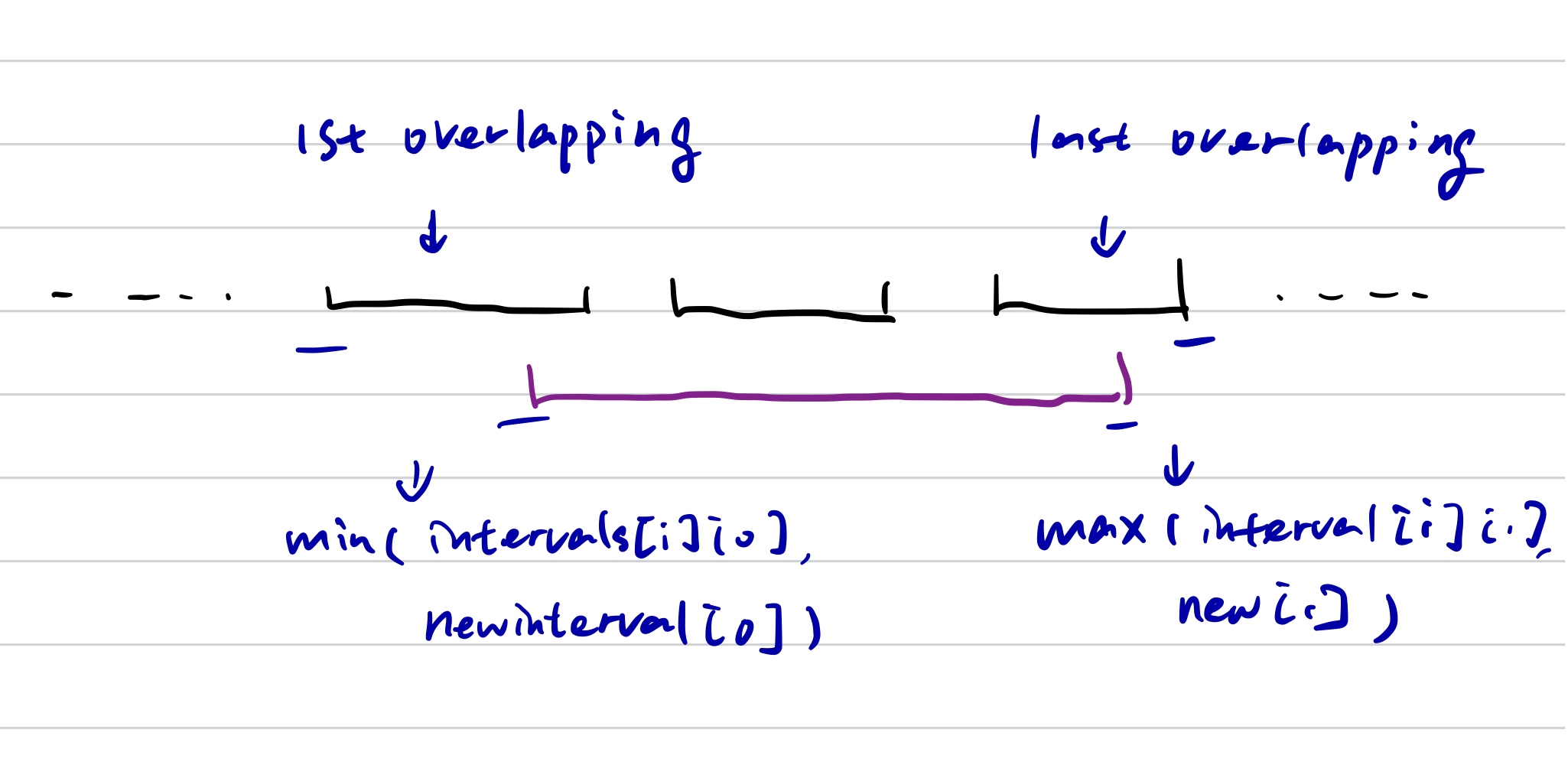
- firstly, we find out the interval whose end is larger than the new inserted interval start (the first overlapping interval)
- start from this first overlapping interval, we find the last overlapping interval, whose start <= new interval’s end
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class Solution:
def insert(self, intervals: List[List[int]], newInterval: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]
i = 0
while i < len(intervals) and intervals[i][1] < newInterval[0]:
i += 1
while i < len(intervals) and intervals[i][0] <= newInterval[1]:
newInterval[0] = min(intervals[i][0], newInterval[0])
newInterval[1] = max(intervals[i][1], newInterval[1])
intervals.remove(intervals[i])
intervals.insert(i, newInterval)
return intervals
1094. Car Pooling
A car with capacity seats. Given an array trips where trips[i] = [numPassengers, from, to] indicates that the ith trip has numPassengers and the location to pick them up is from, drip off is to. Return True if it’s possible to pick all passengers for all the given trips, or False otherwise.
Example:
Input: trips = [[2,1,5],[3,3,7]], capacity = 4
Output: false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
class Solution:
def carPooling(self, trips: List[List[int]], capacity: int) -> bool:
timestamp = []
for trip in trips:
timestamp.append(trip[1], trip[0])
timestamp.append(trip[2], -trip[0])
timestamp.sort()
used = 0
for time, passenger_change in timestamp:
used += passenger_change
if used > capacity:
return False
return True
We can also use diff array to resolve this problem.
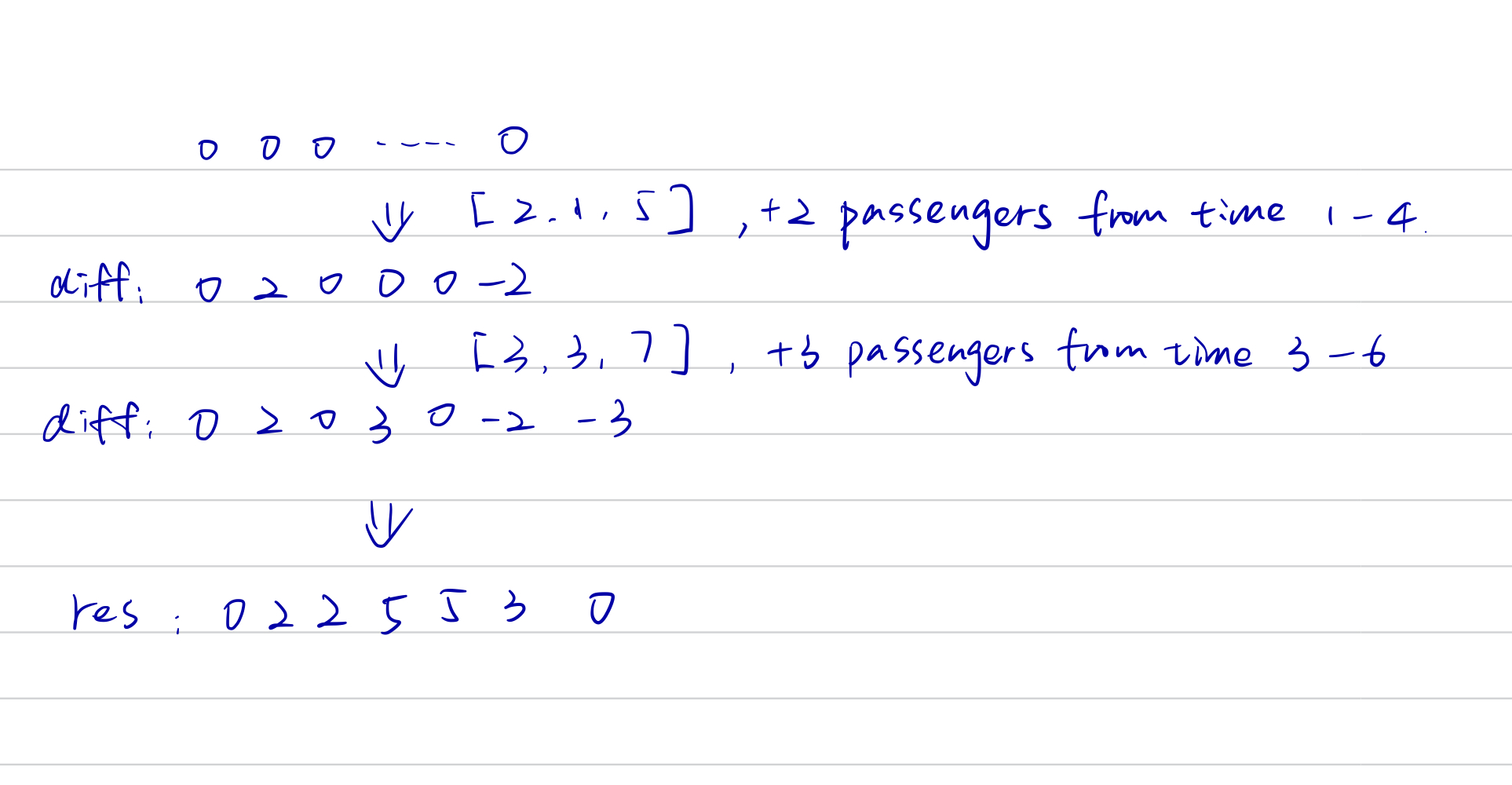
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution:
def carPooling(self, trips: List[List[int]], capacity: int) -> bool:
diff = [0] * 1001 # the problem constraints from and to are less than 1000
for change, from, to in trips:
diff[from] += change
diff[to] -= change # the passengers drop off at "to", so the minus change should happen on "to" time instead of to+1 time
prev = 0
for val in diff:
if prev + val > capacity:
return False
prev = prev + val
return True
1272.Remove Intervals
Given a sorted list of intervals and an interval toBeRemoved, return the set of real numbers with the interval toBeRemoved removed from intervals.
Example:
Input: intervals = [[0,2],[3,4],[5,7]], toBeRemoved = [1,6]
Output: [[0,1],[6,7]]
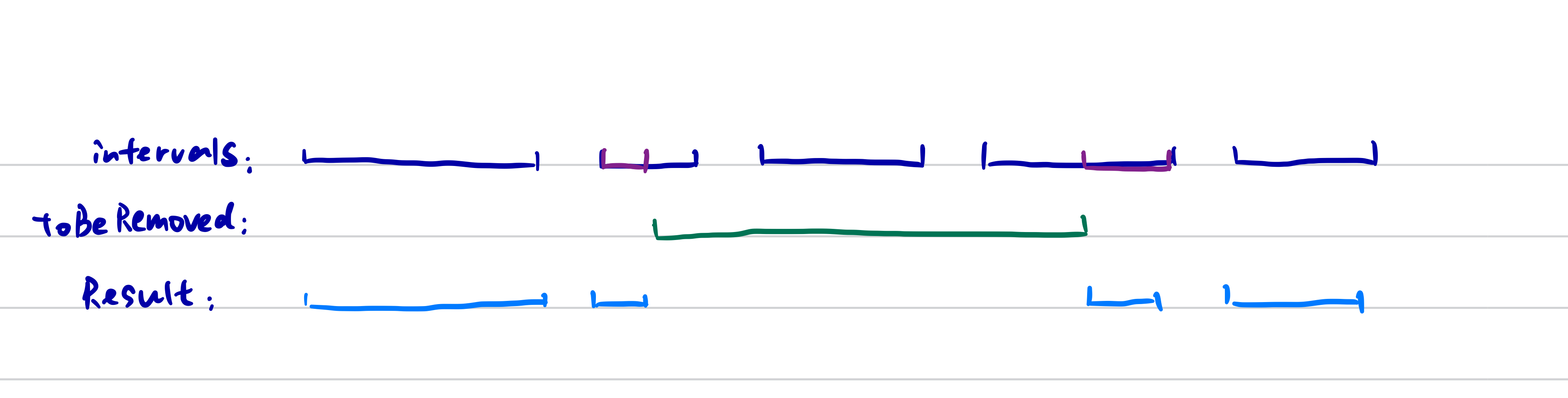
If not overlap, add the current interval to res If overlapped, check whether interval[0] < toBeRemoved[0] and interval[1] > toBeRemoved[1]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class Solution:
def removeInterval(self, intervals: List[List[int]], toBeRemoved: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
for start, end in intervals:
if toBeRemoved[1] < start or toBeRemoved[0] > end:
res.append(interval)
else:
if start < toBeRemoved[0]:
res.append([start, toBeRemoved[0]])
if end > toBeRemoved[1]:
res.append([toBeRemoved[1], end])
return res
435. Non-overlapping Intervals
Given an array of intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], return the minimum number of intervals you need to remove to make the rest of the intervals non-overlapping.
Example:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation: [1,3] can be removed and the rest of the intervals are non-overlapping.
This problem can be solved by DP or Greedy.
For Greedy algorithm, we can solve the array by its end time, and for the overlapped intervals, we always keep the interval whose end time is the minimum to reserve more space for latter intervals.
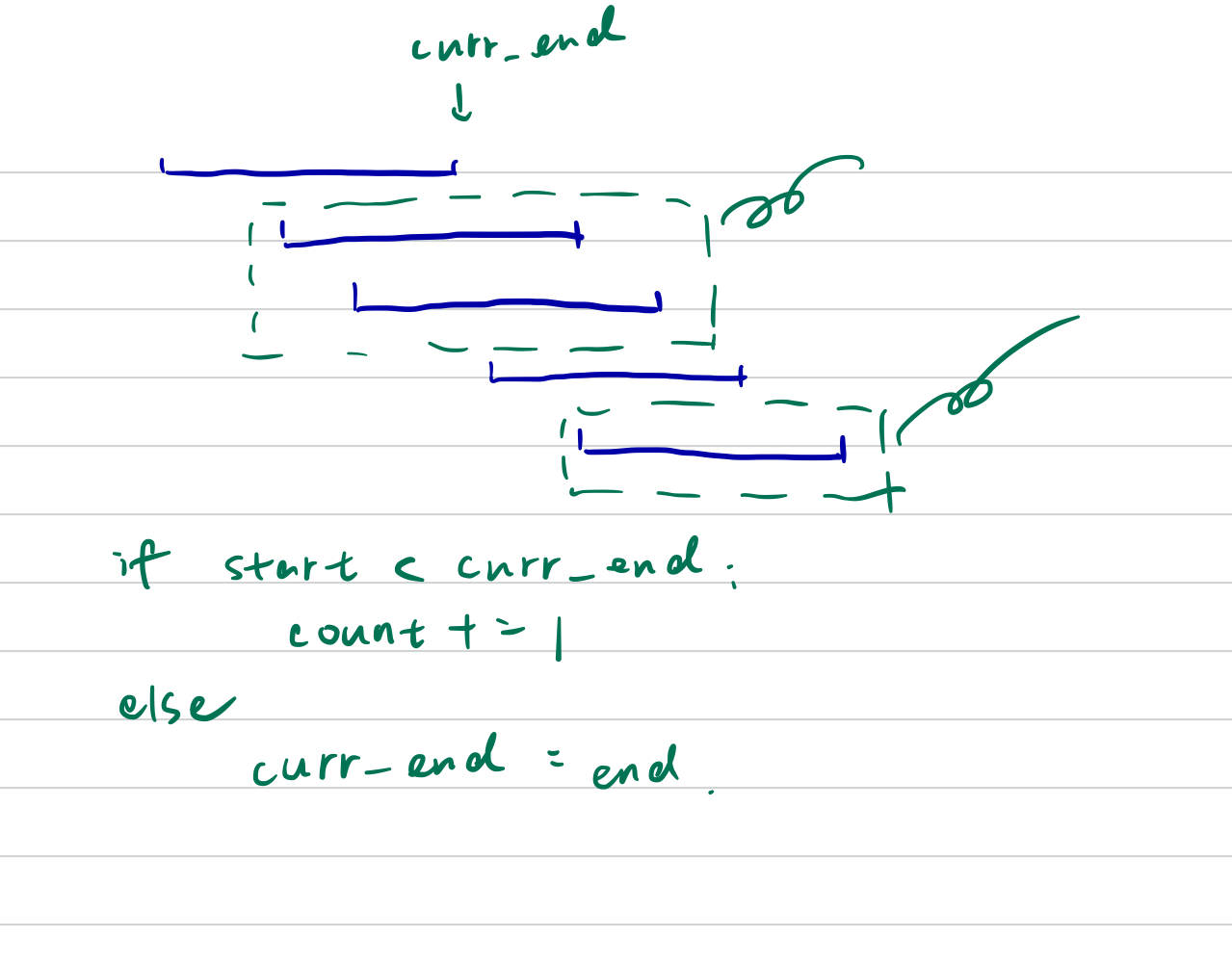
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Solution:
def eraseOverlappingIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
intervals.sort(key = lambda x: x[1])
count = -1
curr_end = intervals[0][1]
for start, end in intervals:
// overlap
if start < curr_end:
count += 1
// new interval not overlap with the former one
else:
curr_end = end
return count
452. Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons
There are ballons on the flat wall. points[i] = [$x_{start}, x_{end}$] who strech from $x_{start}$ to $x_{end}$. A ballon burst if an arrow shot between $x_{start}$ to $x_{end}$. How many arrows do we need to burst all ballons?
Example:
Input: points = [[10,16],[2,8],[1,6],[7,12]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The balloons can be burst by 2 arrows:
- Shoot an arrow at x = 6, bursting the balloons [2,8] and [1,6].
- Shoot an arrow at x = 11, bursting the balloons [10,16] and [7,12].
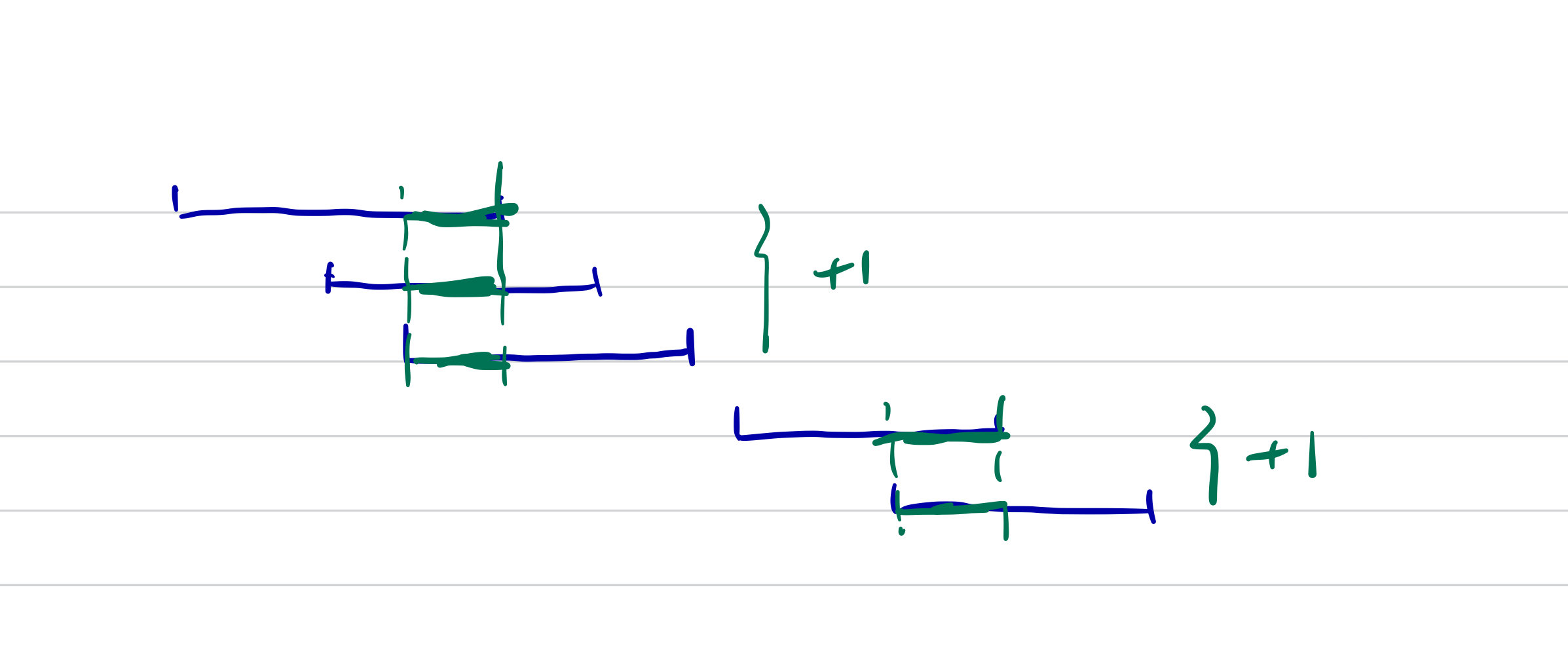 This problem is similar to the non-overlapping problem. We sort the points by its end, whenever we find a new overlap we increase count by 1.
This problem is similar to the non-overlapping problem. We sort the points by its end, whenever we find a new overlap we increase count by 1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class Solution:
def findMinArrowShots(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
points.sort(key = lambda x: x[1])
count = 1
curr_end = points[0][1]
for start, end in points:
if start > curr_end:
count += 1
curr_end = end
return count
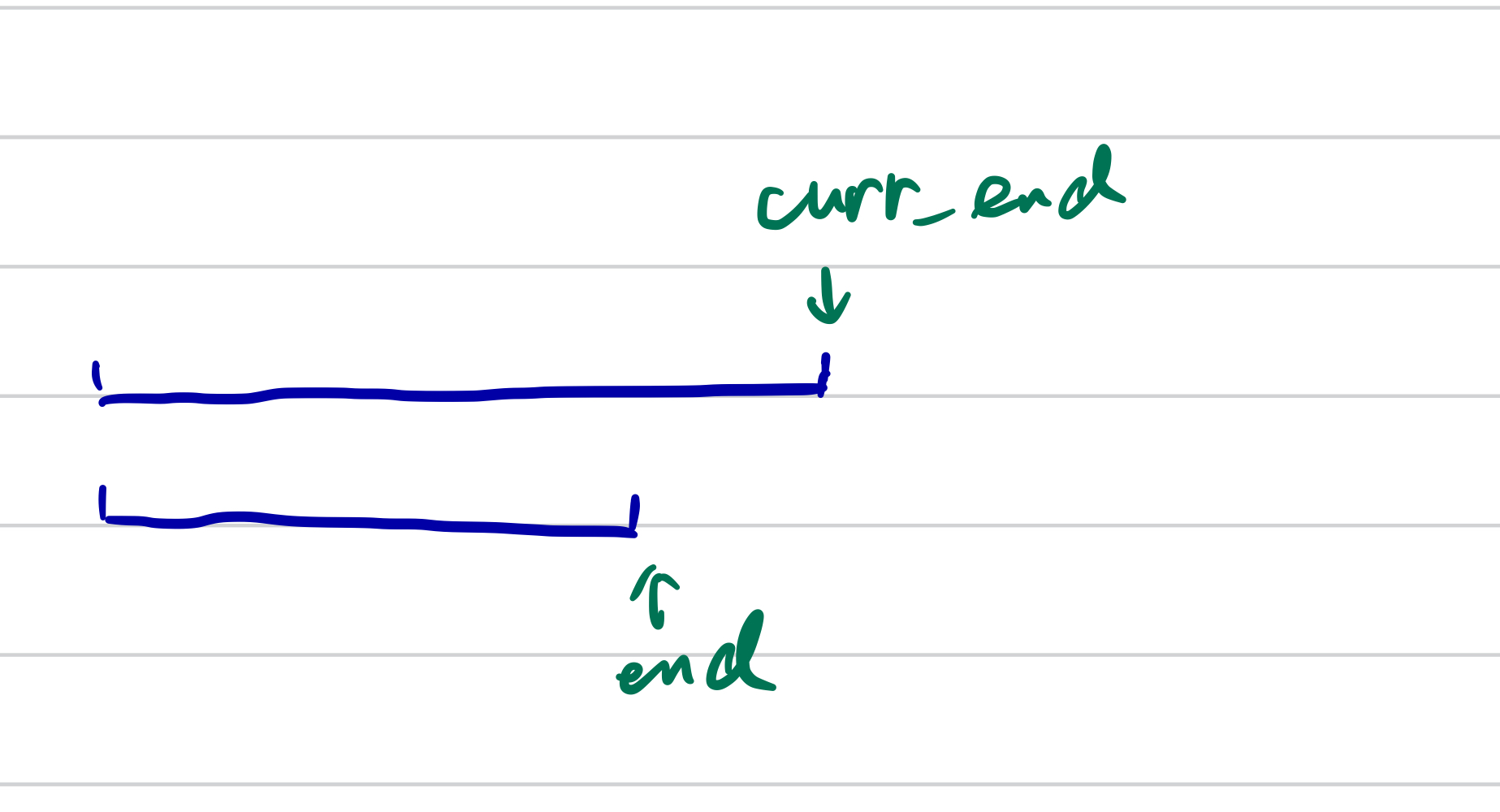
1288. Remove Covered Intervals
Given an array intervals where intervals[i] = [li, ri] represent the interval [li, ri), remove all intervals that are covered by another interval in the list.
The interval [a, b) is covered by the interval [c, d) if and only if c <= a and b <= d.
Return the number of remaining intervals.
Example:
Input: intervals = [[1,4],[3,6],[2,8]]
Output: 2
Explanation: Interval [3,6] is covered by [2,8], therefore it is removed.
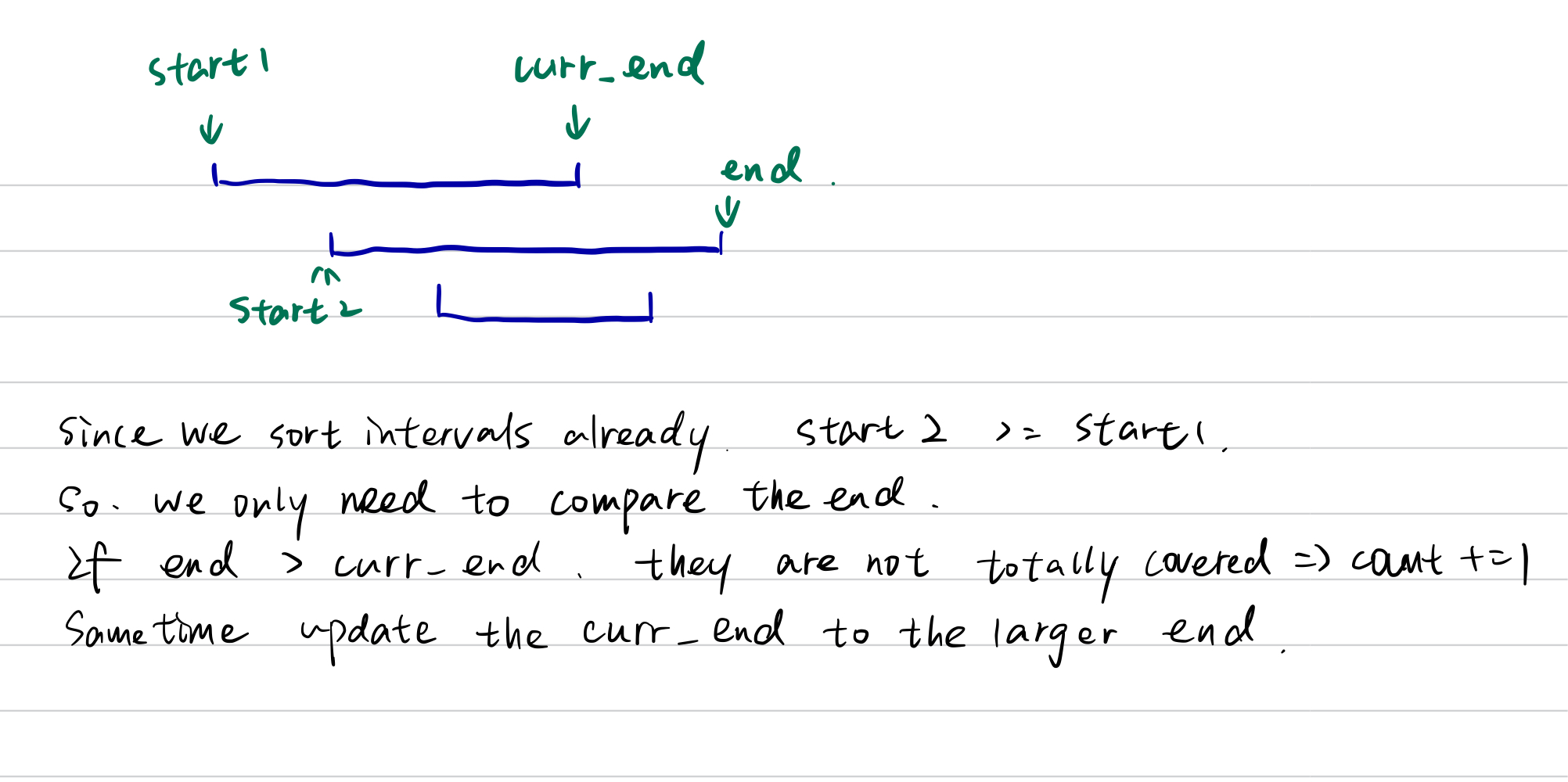
What we need to pay attention is the when sorting, we should sort the end descendingly incase we have intervals with same start.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution:
def removeCoveredIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# sort start ascendingly and end descendingly
intervals.sort(key = lambda x: (x[0], -x[1]))
count = 1
curr_end = intervals[0][1]
for start, end in intervals:
if end > curr_end:
count += 1
curr_end = end
return count
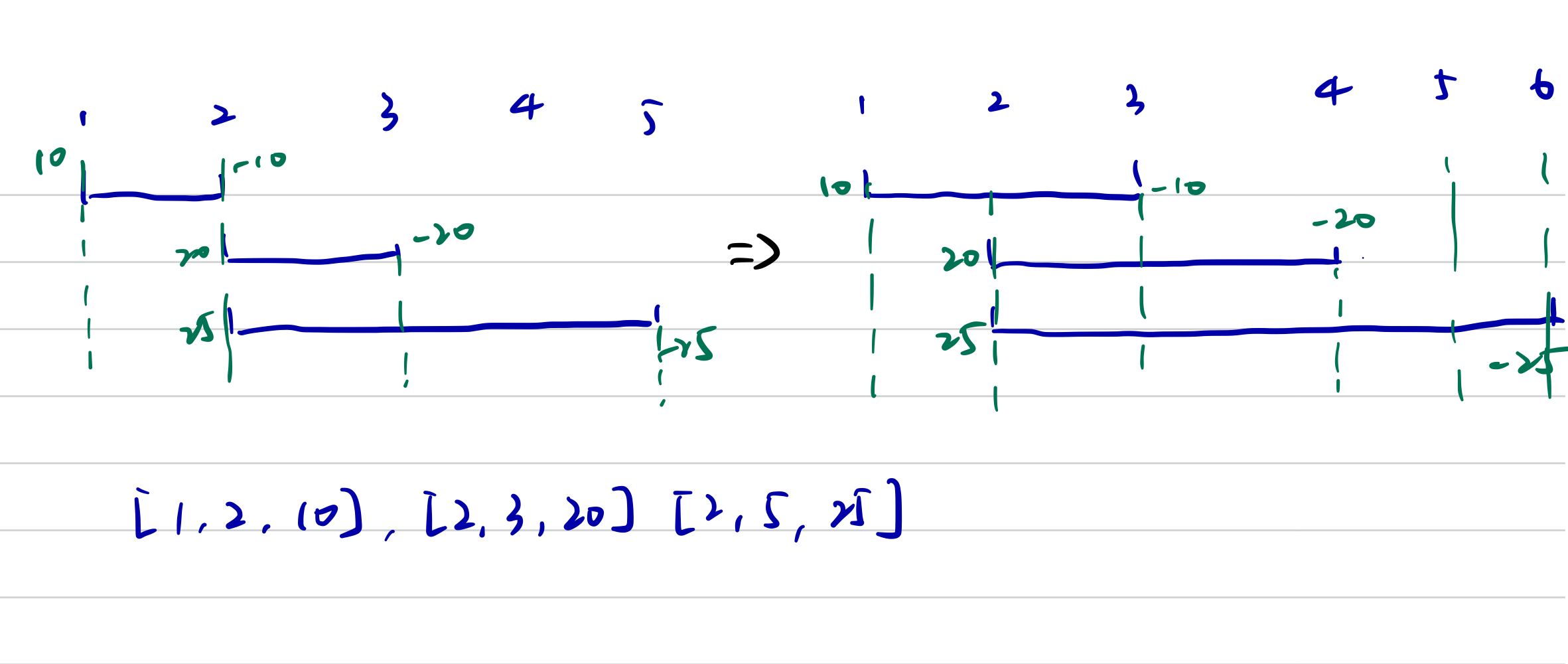
1109. Corporate Flight Bookings
There are n flighs labled from 1 to n.
Given an array of bookings, bookings[i] = [first, last, seats] represents a booking for flights first through last(inclusive) with seats reserved for each flight in range.
Return an array of length n, where answer[i] is the total number of seats reserved for flight[i]
Method1 SweepLine
- Since the seats last is inclusive, the minus change should happen on last + 1.
- If the time are the same, we can add them together than add it into the res list
- The indices start from 1, so need to minus 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution:
def corpFlightBookings(self, bookings: List[List[int]], n: int) -> List[int]:
res = []
timings = []
for start, end, seats in bookings:
timings.append([start-1, seats]) # minus 1 because the bookings indices start from 1
timings.append([end, -seats])
timings.sort()
curr_sum = 0
curr = 0
for i in range(n):
while curr < len(timings) and timings[curr][0] == i: # for all changes at time i
curr_sum += timings[curr][1]
curr += 1
res.append(curr_sum)
return res
Method2 Diff Array
It’s easier if we use diff array to solve this problem, which is almost the same as the carpool problem.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution:
def corpFlightBookings(self, bookings: List[List[int]], n: int) -> List[int]:
res = []
diff = [0] * (n+1)
for from_, to, seats in bookings:
diff[from_-1] += seats
diff[to] -= seats # the change happens on to time
prev = 0
for i in range(n):
res.append(prev + diff[i])
prev = prev + diff[i]
return res